Enhancing Your WiFi Experience: 10 Ways to Improve WiFi Reception
10 Ways to Improve WiFi Reception
Do Boosters Work for WiFi? Debunking Common Myths and Unveiling the Truth
In our hyper-connected world, a stable and fast WiFi connection is essential for seamless communication, work, and entertainment. However, many of us have experienced frustrating dead zones and weak signals within our homes or offices. To tackle this issue, WiFi boosters have become popular solutions to extend and amplify the reach of our wireless networks. But do these boosters truly work? In this article, we will explore the efficacy of WiFi boosters, debunk common myths, and shed light on the truth behind their functionality.
How Accurate Are Cell Phone Coverage Maps?
Cell phone coverage maps can provide a general indication of the expected coverage in a given area, but their accuracy can vary.
Why is AT&T's MicroCell Dropping Calls?
Read more at the AT&T Wirless Forum
Related Posts:
Call Failed or Dropped Calls?
How to Extend iPhone Battery Life & Signal
Top Tips to Improve Your Phone's Signal Strength
Get a Verizon network extender.
People who have Verizon wireless will love this solution to
boost their cell phone signal. It is because, at present, Verizon is the only
network that still offers a network extender. Also known as a microcell or
femtocell, a network extender is a device that Verizon sells to create a better
signal strength at your home. It will route all the cellular calls and the data
over the broadband internet. Please bear in mind; there are a few downsides to
using network extenders, such as the call handoff problems, but if you do not
have an existing cell signal outside, this can be quite a suitable
option.
'I have been a Verizon wireless user for long, and the extender
has wholly resolved my call drop issues, shares Dave, a TrueBlueFishermen associate.
Take your phone higher.
The reception of cell phones better when you travel higher. It
is because if there are buildings around, they can block your signal. So, if
you are in a valley or at the foot of the hill, start climbing. If you are
indoors, you can travel upstairs and travel to the side that receives the best
reception.
Check your phone for any possible damage.
At times, when you drop your phone, despite your phone being in
a case, it can lead to damage to the internal antenna. This will have a severe
impact on the cell signal quality. So, it won't hurt to remove the phone's case
and inspect it for damage. Carefully examine both the corners and the back.
Alternatively, you can even schedule a free appointment with your carrier, and
they can perform a diagnostic on your phone. It will help them confirm whether
the hardware is properly functioning or not. Justin, an employee with MyPlumberschoice, shares
that 'In my Apple, there was a hardware issue, which was hampering my cell
reception. Since my phone was under warranty, they replaced my phone for free,
and now the problem is solved.'
Do not let your phone battery reach to critically low.
At times, when the phone attempts to connect to the nearest cell
phone tower, it tends to suck up all the battery from your phone. When the
battery is already low, it gets hard for the phone to look for a signal. Why?
By default, our phones are programmed to consume minimum battery when searching
for a network, especially when the battery is already low. Hence, it is unable
to perform the task adequately, and this results in poor reception. Thus, it
would help if you did everything you possibly can to conserve your phone's
battery power. For this, you can turn off the NFC and Bluetooth. Also, use
these features only when required. Also, keep the screen brightness to a
minimum, ensure that no software or applications are running in the background
that consumes your phone battery. Also, while you are traveling, it is
inevitable for the battery to go low. So, in this case, carry a portable
charger along.
Remove your phone's case.
If there is a case covering on your phone, only removing it
might better your phone's signal strength. At times, a case may block the cell
phone signal and curtail it from reaching the internal antenna. So, try
removing the case to see any improvement in reception.
Get a new SIM or clean your existing one.
If you have used your carrier for a long time, your SIM card may
not have adequate data to connect to the latest network systems. At times, its
contact may be wearing down or dirty. This may result in intermittent failures.
So, pop your SIM card out, and clean the metal surface using a cotton swab
rubbed in alcohol or a disinfectant wipe.
'Since my cell signal used to be continually weak, I requested
my carrier's support representatives to give me the latest SIM, which helped
better my signal strength,' shares Alexa, an associate with RazorHood.
Yes, we agree with Alexa on this. At times, changing to a newer
SIM can also improve your signal strength. Usually, your network providers will
grant you a new SIM for free.
Shop for a cell phone signal booster
This is the only certified solution, which is majorly
recommended by all the key carriers and the FCC. A cell phone signal booster
will catch all the existing signals outside your phone, amplify its strength,
and then transmit this stronger signal into your home, vehicle, or business.
The good thing is they work with all networks. So, there is no need to shop for
different cell phone signal boosters. More so, it is a one-time investment, and
there is no recurring fee.
Keep your phone's software updated.
At times, the phone may be experiencing signal issues because
you are running your phone on old software. Consequently, the phone may not
perform at an optimal level. It may not have the newest optimizations for
calls, bug fixes, data, or even routine operations. So, before trying every
other method here, this should be the first thing that you do.
Disable LTE if a single bar shows
The bars you see on your phone are determined by things, such as
– load and quality on the nearby tower and the signal strength. If you see a
single LTE bar, it means that the tower from where you are getting your signal
is over-congested. Consequently, it affects the signal quality, resulting in it
being significantly low. In this case, you can consider switching off LTE and
using 3G for a bit. Since most people will be using LTE, 3G will be less
congested, thereby giving you better signal strength.
Get yourself a new phone.
When you have an old phone, particularly one that supports just
3G and not LTE, you should consider shopping for the latest phone. If you
cannot afford the latest phone, even a version or two older models that support
LTE will suffice. This, in itself, can better your data speeds and voice
calls.
Make the most of the Wi-Fi Network.
'I have always had cell signal issues, but this Wi-Fi calling
has completely metamorphosed the things for me,' shares Robin, who did a CDR review online.
Well, yes, this is one of the most excellent solutions that are
hugely prevalent today. Almost every carrier in the USA and Canada, and even
the other parts of the world, offer this new and updated feature of Wi-Fi
calling. As part of this feature, you can now use your internet connection to
surf the internet and simultaneously make phone calls through your phone
network. Please know that Verizon and AT&T offer this feature currently for
Samsung Galaxy, LG, and iPhone users only. However, if you have subscribed to
Sprint and T-Mobile, Wi-Fi calling is available on almost every model. You can
find this option in the settings menu of your phone.
Toggle the Airplane Mode
Lastly, if you are not receiving a signal on your phone, you can
toggle the Airplane mode once, wait for about five to ten seconds, and turn it
off again. This can help you better your reception.
So, these are some of the most effective ways to better weak cell reception.
Identifying Dropped Call Locations
How To Check For Cell Phone Coverage By Address
When it comes to choosing the best mobile operator, most people think of the Big Three. The Big Four are known as AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile / Sprint. However, but they should also include a number of other smaller MVNO carriers that use these major networks.
All four networks are available in the US, with AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, Sprint each having their own LTE networks. According to paid studies most carriers will claim they have coverage everywhere but we know this is not true. Coverage only matters at your home address and the only way to check this is by asking someone else in your area, trying it out, or by looking at coverage complaints submitted by customers on the cell phone coverage reviews map above or on the check cell coverage by address mobile map.
You can search this map to see which areas have the worst overage on each of the four major networks in the United States. Use the small search circle in the lower left-hand corner of the map. This map allows you to filter coverage reviews of all major mobile networks by simply clicking on the carrier on the right-hand side of the map.
Enter your country, city, postal code, home or office address select your current location, filter by carrier type and region, and select the best and worst coverage in your area for each of the four major networks in the United States. In this example, you choose one of four different types of mobile towers for the USA and specify a country.
Use can other tools like RootMetrics, OpenSignal, CellReception.com, or SignalMap to see what others are reporting about the range of the operator in your area based on positive signal strength. However, these providers do not allow you to provide reviews on carriers in specific locations. There is also a map to look at cellular towers and antenna locations nearby.
RootMetrics does not have a map of the mobile towers in the viewfinder, but in some areas, it shows the cell signal quality. Although Root Metrics does not have a map of mobile towers, it is a strong indicator of signal quality in your area.
T-Mobile Tower Map lets you enter your zip code, locate a location on the map, and see if 4G LTE coverage is available. Search for T-Mobile 5G coverage from your current location, and it's available in all 50 states and Puerto Rico.
Sprint gives you the ability to look up any address you want and allows you to see the coverage that's in your location. To access the website you are using, such as T-Mobile Tower Map, first, enter your address in the search engine of our website. Go to our mobile phone comparison engine and check the coverage at your exact location, and you will begin to gain a better understanding of coverage at the sites you are using.
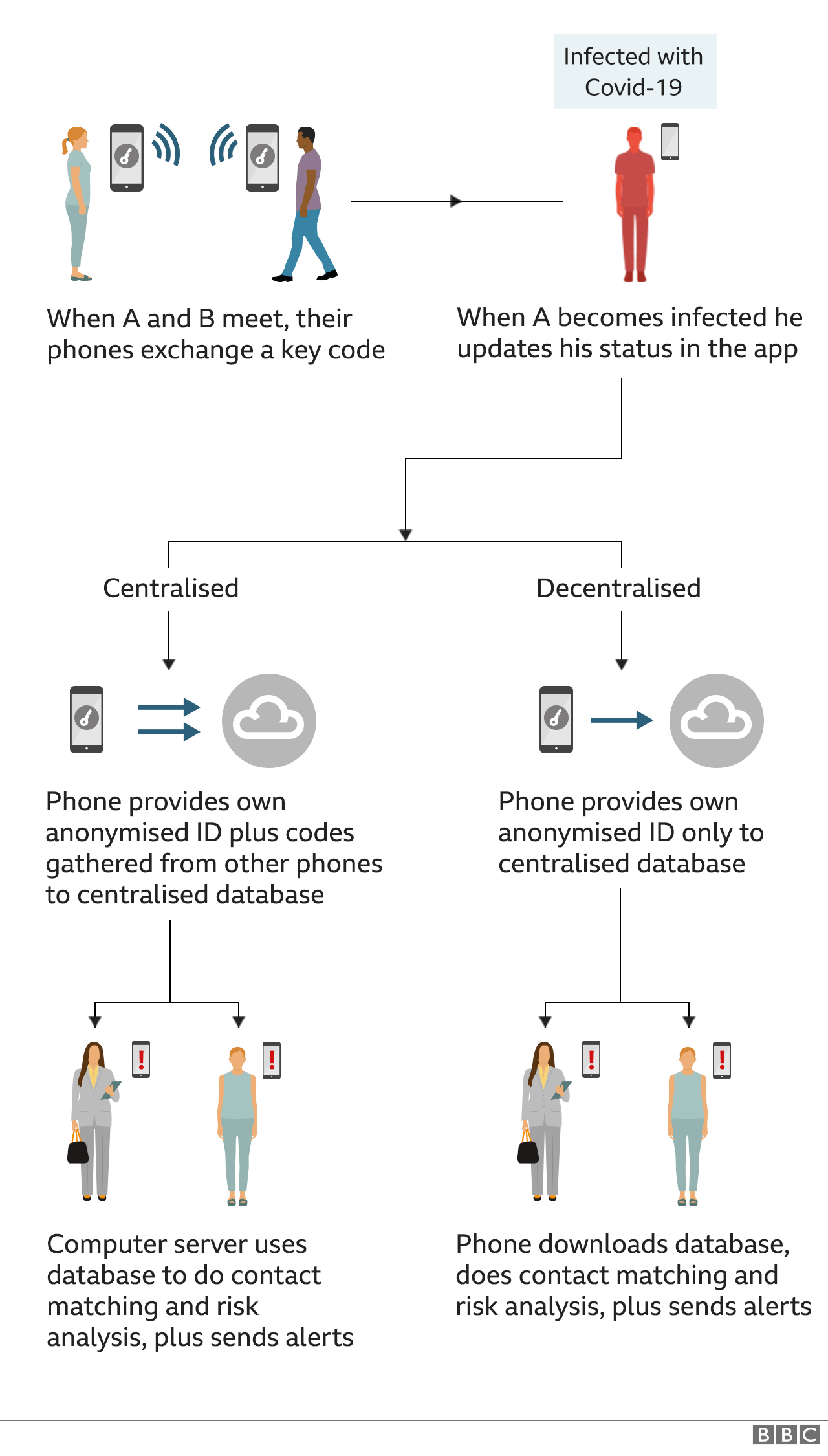
How Does Cell Phone Contact Tracing Work?
The Apple-Google model carries the process out on the handsets themselves, making it more difficult for the authorities or potential hackers to de-anonymize the records and use them for other means.
Digital contact tracing replaces at least some of those interviews with technology. Especially in South Korea and China, it's been an effective way to keep infections down. (South Korea is finally down to zero local infections.) But the successful approaches used elsewhere rely on a level of trust in authority and giving up privacy, which may not be acceptable in the individualistic United States.
Your mobile phone carrier can track your location at all times, by analyzing cell tower connections. This depends on the cell signal strength. In South Korea, when someone is diagnosed with COVID-19, those tower hits are being shared with local governments, which combine them with CCTV footage, credit card receipts, and interviews, and broadcast the results on the web and through text messaging.
Bluetooth-based contact-tracing apps such as Singapore's TraceTogether rely on phones running the app in the background, searching for nearby Bluetooth devices also running the app—that's how Apple's AirDrop works. Phones can roughly determine the distance between each other based on Bluetooth signal strength; recent iPhones can also use their U1 ultra-wideband chips to figure out their proximity to each other. Unlike the network and QR-code-based solutions, Bluetooth-based apps drain your phone's battery.
6 Easy Ways to Boost Your Mobile Phone Signal
Why Your Home Cell Phone Signal Has Stopped Working
Improving Cell Signal for United States Cellular Networks
Solutions for Weak Cell Phone Signals at Home

To improve cell signal for your home, you’ll want to start by answering the following questions to better assess your needs.
· If your reading is -94 to -104 dBm you are in a gray zone; you may be able to use a signal booster but may also require a femtocell.
The solution to boost the cellular signal for a two-bedroom apartment will likely be different from the solution for a five-bedroom home or 12,000-square-foot mansion. Signal boosters tend to provide a usable signal to larger coverage areas whereas femtocells are generally used in small spaces the size of one to two rooms.
Think about how much area within your home will need to have reliable cellular signals. Depending on the solution you select and the signal outside of your building, you may only see an improvement in a small area. If a small area of coverage is sufficient, a femtocell may be a suitable solution. On the other hand, if you have a moderate outside signal, a signal booster may be able to repeat that signal throughout your home.
Your pricing options range from a few hundred dollars for a femtocell or signal booster that can support small spaces to $1000 for very large homes. For signal boosters that can cover very large homes, the cost can exceed $1000 and may require a cellular system design service, which SureCall provides free for buildings above 10,000 square feet. Your cellular provider may offer you a free (or discounted) femtocell solution to enhance your signal within a small area of your home. To pursue that option you’ll need to contact your provider.
If you have poor reception with your cellular provider but have friends or family who have better reception with a different cellular carrier, you may want to consider transferring carriers. There can be early contract termination fees if you are not at the end of a contract term. Check with your cellular provider for their contract termination fee or to see when your existing contract expires.
Femtocells are the ideal solution for homes with no cellular reception, which we consider readings lower than -100 dBm. In most instances, femtocells will enhance cellular signal for a small space, but typically not much more than one to two small rooms.
Femtocells cost between $100 and $400 and require a monthly subscription that will be added to your internet bill. Your cellular carrier may provide this for free, but this is very situational and something you shouldn’t depend on.
Also known as bi-directional amplifiers (BDA) or repeaters, cell phone signal boosters come in kits that include an outdoor antenna, indoor antenna, signal booster, and cabling to connect and power the system. Some kits may combine the indoor or outdoor antenna and booster for a minimalist appearance in your home.
Cell phone signal boosters work by capturing the signal that exists outside of your home with an outdoor antenna before feeding it to the signal booster. The signal booster then amplifies the signal strength and sends it to the indoor antenna to transmit the signal inside of your home.
Some signal boosters are more powerful than others, and the coverage area will primarily depend on the signal that exists outside of your home and density of internal walls and building structure.
Generally, with a clear line of sight, signal booster kits with a Yagi outdoor antenna can reach towers up to 40 miles away, whereas Omni-directional outdoor antenna kits reach towers up to 20 miles away. This range is dependent on the strength of the signal leaving the tower and the number of obstacles between you and that tower.
Signal boosters cost around $300 for small homes and apartments, around $400 to $600 for large homes, and around $1000 for very large homes. These kits can be customized with different indoor antennas to adapt to the layout of your home and outdoor antennas to adapt to the distance between you and the nearest cell phone tower.
Both femtocells and cell phone signal boosters present strong solutions that, given your cellular circumstance, can take you from weak or unusable cellular signals to strong signals. If you have any questions, we suggest doing your research on SureCall, a top signal booster manufacturer. Check out all of SureCall’s cell phone signal boosters for home.
Does Rootmetrics & OpenSignal Drain Battery Life & Memory?
Sensorly, OpenSignal, MyMobileCoverage, or Rootmetrics apps basically turn your cell phone into a signal meter so you can measure your 4G & 5G cell signal strength. These apps run in the background of your phone and send data to the provider. They all aggregate the data and provide a theoretical coverage map.
Is RootMetrics Data Too Expensive?
 |
| RootMetrics vs DeadCellZones Map |
RootMetrics claims to drive test (test signal strength) in under 100 markets twice per year. Drive testing makes sense but it is anecdotal data and only a snapshot at that time. Can RootMetrics possibly drive test during every rush hour in every location? No! Do RootMetrics have actual customer complaints? No! Are they drive testing in rural and undeserved marketing? No! Do their maps tell you where problems exist? Kind of.
Which map tells you more about where problems exist? What RootMetrics doesn't have are actual customer coverage complaints like what we publish on Deadcellzones.com. We get 3,000-5,000 people per day that visit our web site and contribute dead zones directly to the map.
If you are looking to purchase data from RootMetrics than you most certainly should also look at purchasing our crowdsourced Dead Zone data. Positive signal strength data and negative signal strength information can be quite complimentary. Contact us for further details on pricing and why we can help you save money.
Can You Drive Testing Indoor Coverage?
Wireless service providers (especially in the U.S.) do drive testing to build theoretical coverage maps and test their networks for cell signal strength. Drive Testing or wireless data collection is used to provide coverage analysis, network weakness information and to aid in finding specific problem areas reported by consumers. Most drive testing companies are specifically tasked with simulating the actual call experience of customers during weekday periods to simulate capacity issues outdoors. Such companies include GWS, LCC, and WFI. Most carriers outsource this capability to third parties, unlike Verizon who has its own in-house drive testing team. Drive testing companies usually spend between $15-25 per mile in over 300+ U.S. markets benchmark testing signals. These companies provide a tremendous service to the carriers and deserve every penny for their efforts but how do they efficiently acquire in-building coverage data where customers use their phone the most?
DeadCellZones.com will be a the forefront of the carrier femtocell revolution and will start helping drive testing companies get better visibility of in-building coverage problem areas. U.S. carriers are starting to roll out femtocells and the number of worldwide subscribers is rising rapidly, jumping from 1.7 million in 2007 to 9.7 million in 2008. The number of femtocell phone units is expected to nearly quintuple in the 5 years from 2007 to 2011.
 I think the current recession is going to demand cost-cutting measures that we have never seen from these companies since churn is more prevalent than customer growth. The carnage could be huge from suppliers and vendors beneath the umbrella of these giant companies of those who do not innovate. Its widely known throughout the industry that working with carriers is not much different than working with government bureaucrats because of their proprietary networks and huge customer bases. The lack of leadership of the wireless communication giants to is the primary reason why the U.S. is way behind Europe and Asia in wireless telecommunications.
I think the current recession is going to demand cost-cutting measures that we have never seen from these companies since churn is more prevalent than customer growth. The carnage could be huge from suppliers and vendors beneath the umbrella of these giant companies of those who do not innovate. Its widely known throughout the industry that working with carriers is not much different than working with government bureaucrats because of their proprietary networks and huge customer bases. The lack of leadership of the wireless communication giants to is the primary reason why the U.S. is way behind Europe and Asia in wireless telecommunications.Bluetooth Beacons Are Used Like Mobile Phone Cookies
Bluetooth proximity marketing is the latest marketing technique being deployed by retailers, Governments and sporting venues to track users. How these groups benefit from it? They do it through proximity marketing and it is about connecting with your audience at the right place and time.
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless system found on most smartphones and tablets that transmit information and can receive information. Most people currently use Bluetooth for hands free in our cars or to connect to a wireless speaker. Bluetooth proximity marketing involves setting up Bluetooth "broadcasting" equipment at a particular location. If your Bluetooth is "turned on" and you are near one of these beacons. Information can be sent to devices via be text, images, audio on enabled devices (aka cell phone, tablet) within range of the transmitter (beacon). A Bluetooth enabled mobile device, when in range of the beacon (transmitter) receives the signal and then via the device's operating system, passes information to the appropriate mobile app(s).
Several things need to happen beforehand.
1) Bluetooth is turned on
2) A Bluetooth beacon transmitter must be nearby
3) The targeted individual should have a specific application installed on the their phone that is capable of receiving a push notification.
What information is collected?
1) The ID of the phone and user of the phone
2) Cellular or Wifi signal strength issues
3) Locations traveled of other beacons in the area (for example locations within a store).
Popular Posts
-
Boost Mobile Coverage Map Boost Mobile is a prepaid wireless service provider in the United States. It offers no-contract cell phone ...
-
As WiFi becomes more essential to modern homes, many people wonder how far a WiFi router should be from their sleeping area for safety and...
-
In the rapidly evolving world of mobile connectivity, choosing the right network provider can be daunting. With giants like Verizon, AT...
-
Which State Get The Most Cell Phone Coverage Complaints?
-
Experiencing full bars on your cell phone display but no service can be attributed to several factors:
-
AT&T is one of the largest wireless service providers in the United States, offering a variety of service plans and extensive covera...
-
Starlink, the brainchild of billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk, is revolutionizing global broadband access using an ever-expanding network o...
-
Cell phone service has become an indispensable aspect of daily life. From communication to accessing essential information, the reliability ...
-
Consumer Cellular Coverage Maps on AT&T Consumer Cellular is a prepaid wireless MVNO that operates on AT&T's & T-Mobile...
-
Verizon Wireless is one of the largest wireless service providers in the United States, offering a wide range of mobile plans and exten...